2022 Data Access & Analytics Trendbook
Expert perspectives on where data use is heading


As companies started moving data to the cloud and separating compute and storage for added efficiency, cost savings, and flexibility, data platforms became more advanced and diverse, introducing new categories for best-of-breed technologies. With data engineering and operations teams now accelerating adoption of more than one cloud data platform, according to our 2020 State of Data Engineering and Operations Survey, data architectures have become increasingly heterogeneous and complex. While each cloud service offers its own access control capabilities, in an ecosystem comprising multiple compute platforms, those access controls become disparate and siloed. This prevents consistent data access control across all platforms, leaving data at risk of unauthorized access and use, and making it harder to understand who accessed what data, when, and for what purpose.
Hadoop-era platforms had similar challenges — albeit on a smaller scale — with a few heterogeneous services that were reasonably managed using Sentry or Ranger. However, modern architectures have increasingly diverse workloads in lakehouse architectures, combined with decentralized access control, complex rules for data use, and expanding data consumer varieties. Older approaches to data access control do not scale to meet the requirements for these modern architectures — a new approach is necessary.
Immuta is the universal cloud data access control platform that provides automated access control across heterogeneous compute platforms in lakehouse environments. With our new product release, which includes enhanced integrations with Amazon Redshift, Azure Synapse Analytics, Databricks SQL Analytics, and Trino (formerly PrestoSQL), data engineering and operations teams are better equipped to centralize data access control for increasingly popular lakehouse architectures. With Immuta, data teams can maximize the full value of their cloud investments and meet contractual and regulatory SLAs for data access and usage.

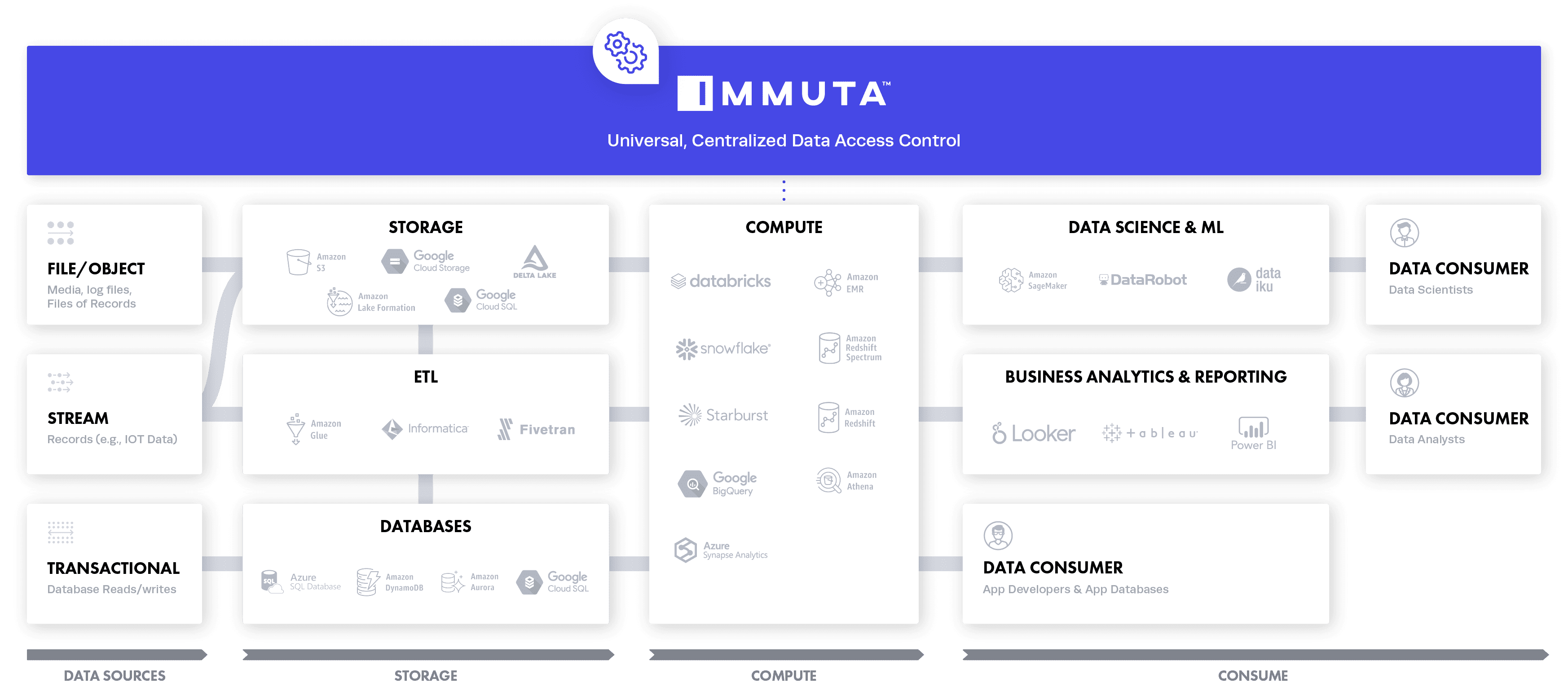
Immuta’s new native integrations with Redshift Spectrum, Azure Synapse Analytics, Databricks SQL Analytics, and Trino join existing native support for best-of-breed cloud technologies, including Databricks, Starburst, Snowflake, and Google BigQuery. By centralizing and providing universal data access control for both cross-cloud and native cloud data platforms, Immuta eliminates manual processes, data copies, proliferation of views, and inconsistent policy enforcement. The result is streamlined data access and use throughout the data lakehouse. Most other access control solutions rely on each data platform’s specific data access control capabilities, which leads to disparate enforcement and unreliable data security and protection. The risks and lack of scalability associated with this approach are substantial, and can halt the utility of a data lakehouse in its tracks.
For organizations looking for an efficient, cost-effective way to power diverse workloads for data engineering, data science, machine learning, and analytics, Immuta is the only solution that offers automated security and privacy controls that are enforced consistently across lakehouse architectures — with no exceptions or enforcement gaps.

Expert perspectives on where data use is heading
Immuta provides essential consistency and stability for organizations looking to derive the most utility and greatest ROI from their data lakehouses.
Integration with all lakehouse architectures
By integrating with a broad scope of cross-cloud data platforms — including Databricks, Snowflake, Starburst, and Trino, and native cloud platforms, like Redshift Spectrum, Google BigQuery, Azure Synapse Analytics — Immuta provides easily scalable, consistent security and privacy controls with complete command of policies across the lakehouse. Our recent survey of data engineers showed that Amazon Redshift and Azure Synapse Analytics were two of the top five platforms that data teams expected to adopt within the next 24 months, so we anticipate the need for this type of universal data access control to continue growing, and even accelerating.
Immuta’s core feature set works consistently to provide fine-grained access control across platforms. This feature set includes sensitive data discovery and classification; scalable access control (role-, attribute-, purpose-based using policy variables); advanced data masking and anonymization; and dynamic policy enforcement and auditing.
Expanded metadata integration
In lakehouse architectures, metadata serves as a single source of truth for consistent policy enforcement — and governing its accessibility is critical. With Immuta’s dbt Cloud integration, data teams can leverage metadata in dbt to enforce policies in real-time. This option joins Immuta’s existing metadata integrations with Alation, Collibra, Informatica EDC, Okta, Sailpoint, and more.
Policy as Code
Additionally, Immuta enhanced its “policy as code” capabilities with a new command line interface (CLI). This enables data engineering and operations teams to fully automate sensitive data management at scale, eliminate inefficiencies, and close policy gaps by seamlessly integrating and codifying cross-platform policy infrastructure with existing DataOps toolchains. The end result is end-to-end stability and efficiency across heterogeneous technologies in a data lakehouse.
Check out my recorded demo showing a global, cross-platform policy that consistently segments data by the user’s region across different tables in Databricks and Redshift, with policies enforced entirely in the platforms. Immuta is the first and only technology available that can do this.
To see how Immuta integrates with your tech stack to achieve universal data access control,
Innovate faster in every area of your business with workflow-driven solutions for data access governance and data marketplaces.